What Should Be The First Intervention in Case of a Heart Attack?
Life is full of unexpected emergencies, and a heart attack is one of the scariest. A heart attack is a condition in which the blood supply to the heart is cut off, causing damage to the heart muscle. Without quick intervention, it can be fatal. So, what kind of first intervention should be done in case of a heart attack?
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack is a condition in which the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients as a result of a blockage in the coronary arteries. Usually, a blood clot forms as a result of plaque build-up in the coronary arteries. This clot prevents blood flow to the heart muscle.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a heart attack usually appear suddenly. The symptoms are as follows:
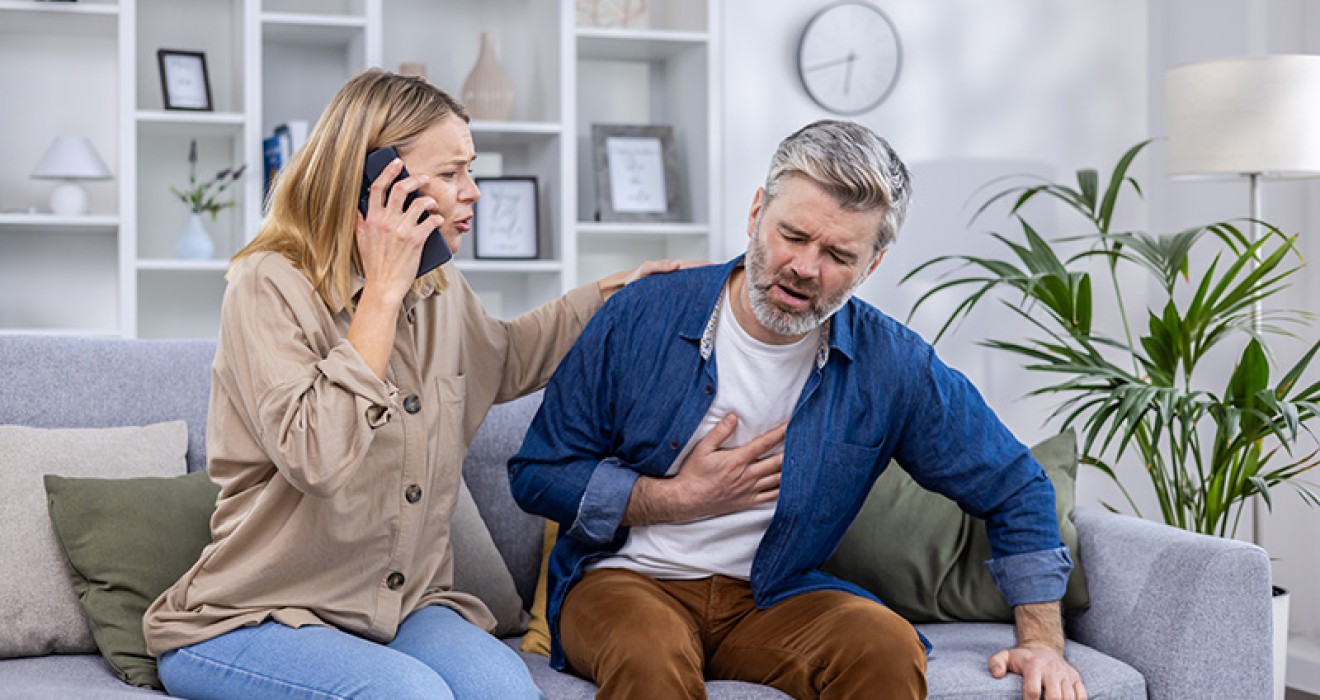
- Chest Pain: A feeling of pressure, tightness or pain in the chest. The pain can often be felt in the left arm, jaw or upper back.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or sudden shortness of breath during an attack.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea, vomiting or stomach pain.
- Dizziness and fainting: Dizziness, weakness and fainting may occur.
- Cold sweating: Cold and clammy skin.
- Fatigue and weakness: Sudden and unexplained fatigue and weakness.
These symptoms are usually seen together.
First Intervention During a Heart Attack
First interventions during a heart attack can be life-saving. Intervention methods are as follows:
- Call for Emergency Help: When you notice the symptoms of a heart attack, you should immediately call for emergency help. Call 112 or the local emergency number and explain the situation in detail.
- Assign a Comfortable Position: The patient should sit in a chair or lie down and assume a comfortable position. This can reduce the pressure on the heart.
- Give Aspirin: If the patient is able to take aspirin, they may be offered to chew an aspirin. Aspirin can help dissolve blood clots. However, do not use this method for people who are allergic to aspirin or who need to take aspirin unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): If the patient is unconscious and not breathing, you should perform CPR immediately. To perform CPR, lay the patient on their back on a flat surface. Place the heels of your hands in the center of the patient's chest. Press hard and fast with your hands against the chest. Try to do 100 - 120 compressions per minute. Give two artificial respirations after two compressions. However, if you are not familiar with artificial respiration, you can only do compressions.
- Try to alleviate the pain: If the patient is in pain, take the necessary measures to alleviate the pain. Drugs such as aspirin can help in this regard. However, consider the patient's medical history and possible drug allergies.
- Share Patient Information: When emergency medical teams arrive, share the patient's medical history, current medications and symptoms. This information is critical in the emergency response process.
Precautions Before and After a Heart Attack
Taking some precautions to prevent and manage a heart attack can help protect your health:
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet that promotes heart health. Eat low-fat, high-fiber and low-sodium foods.
- Exercise Regularly: Try to get at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week. Exercise strengthens heart health and reduces risks.
- Reduce Smoking and Alcohol Use: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of heart attack. Avoid or reduce these habits.
- Avoid Stress: Managing stress protects heart health. You can use meditation, yoga or relaxation techniques.
- Have Regular Health Checkups: Get your blood pressure, cholesterol levels and general health checked regularly. This can help you detect heart disease at an early stage.
In summary, a heart attack is a serious condition that requires immediate intervention. Recognizing the symptoms, taking the right first aid steps and acting quickly can save lives. Keeping your health information up to date and practicing healthy living habits can reduce the risk of heart attack.